Kea2
Kea2应用场景_以微信为例
目前我们的Kea2 具备以下几种关键 Feature:
-
Feature 2.1: 穿透难以越过的页面:尤其是那些需要介入人类知识的业务步骤(如填写表单等)
-
Feature 2.2: 跳出焦油坑(鬼打墙):在实际测试中,自动遍历测试工具会陷入某些局部页面,无法自行跳出(如反复在某个页面进行遍历),Kea2可以让引导自动遍历工具跳出这些页面
-
Feature 3.1: 支持断言测试(基于性质的测试),可自动检查业务逻辑正确性:聚焦核心业务功能逻辑,而不必去关心app启动应该如何到达业务功能,让脚本测试更轻松
-
Feature 3.2: 支持多断言(多性质)联合混沌测试:将刻画出业务功能的性质后,Kea2在测试过程中,可自动组合各个业务功能,从而发现更深层次的业务逻辑错误
接下来我们以微信为被测应用,结合微信的一些具体场景,对Kea2上述Feature进行详细介绍,展示其灵活的测试能力和独特优势。
Feature 2.1:kea2可以穿透自动化遍历测试过程中难以越过的页面
例:微信登录
微信必须在登录之后才能进入应用的主页从而执行其他测试,但传统的自动化测试工具在遍历时很难越过该页面,但kea2可以通过脚本轻松越过该页面从而执行下面的测试。
脚本
# Precondition decorator: Ensure the login page is loaded by checking existence of
# both account input field ("请填写微信号/QQ号/邮箱") and password input field ("请填写密码")
@precondition(
lambda self: self.d(text="请填写微信号/QQ号/邮箱").exists
and self.d(text="请填写密码").exists
)
def test_login(self):
"""Test WeChat login functionality by entering credentials and submitting the login form."""
# Input username into the account field using UI element locator with text "请填写微信号/QQ号/邮箱"
self.d(text="请填写微信号/QQ号/邮箱").set_text("username")
# Input password into the password field using UI element locator with text "请填写密码"
self.d(text="请填写密码").set_text("password")
# Click the login confirmation button with text "同意并登录" to submit the credentials
self.d(text="同意并登录").click()
截图

解析
前置条件:
- 当微信登录页面中存在 “请填写微信号/QQ号/邮箱” 和 “请填写密码” 输入框时触发测试。
交互场景:
-
输入账号:在“微信号/QQ号/邮箱”输入框中填写固定值 “username”。
-
输入密码:在“密码”输入框中填写固定值 “password”。
-
提交登录:点击 “同意并登录” 按钮。
注:脚本执行完毕之后,微信登录成功,Kea2可以到达微信的主页面从而继续执行下面的测试。而且,在后继的自动化测试过程中,微信如果意外被登出,那么这段脚本就有可能被重新自动执行,再次完成登录。
Feature 2.2:kea2可以引导自动化遍历工具跳出焦油坑,防止遍历工具陷入某个(些)页面中无法自行跳出
例:跳出境外支付页面
遍历工具可能会陷入“境外支付”页面中无法自行跳出,反复在某个页面进行探索,遍历工具必须得连续执行4个“返回”操作才能跳出这些页面,这对于遍历工具而言很难。此时可以让Kea2引导轻松跳出此页面。
脚本
# Probability decorator: This test will be executed with 10% probability during test runs
@prob(0.1)
# Precondition decorator: Verify the test should only run when the text "境外感知支付,一拍即付"
# is visible on screen
@precondition(lambda self: self.d(text="境外感知支付,一拍即付").exists)
def test_jump(self):
"""
Test jump navigation functionality from cross-border payment feature page.
Simulates pressing back button multiple times to return to previous screens.
"""
# Press Android back button once to exit current screen
self.d.press("back")
# Press back button second time to navigate further back
self.d.press("back")
# Press back button third time to continue navigation
self.d.press("back")
# Press back button fourth time to complete the back navigation sequence
self.d.press("back")
截图

解析
前置条件:
当页面中存在文本为 “境外感知支付,一拍即付” 的元素时会以一个较低的概率 @prob(0.1)触发测试。
交互场景:
- 连续四次返回键操作:
- 通过 self.d.press(“back”) 模拟物理返回键,依次退出当前页面层级。
注:脚本执行完毕之后,就跳出了这些相对比较深的页面,退回到了“我的”页面,Kea2可以避免被限在一些难以跳出的页面。
Feature 3.1:kea2可支持断言测试(基于性质的测试)
基于此,我们可以在需要测试某个应用功能时,问三个关键问题:
1、功能的入口在哪里?
2、功能的执行操作是什么?
3、功能的预期行为是什么?
这就是 基于性质的测试。在形式化表述中,我们使用:
前置条件 P:功能的入口
交互场景 I:功能的执行操作
后置条件 Q:功能的预期行为 (assert)
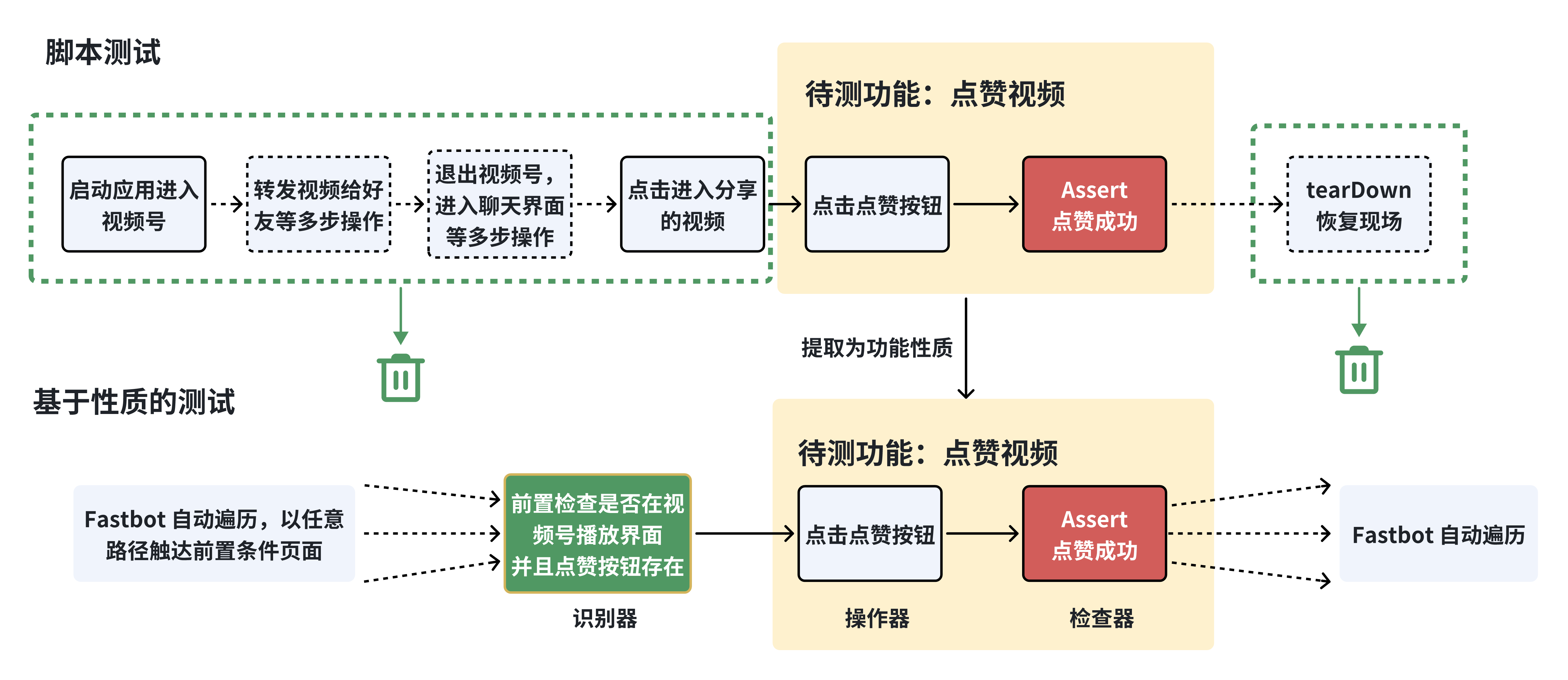
例1:视频号点赞功能
传统测试需手动模拟完整用户路径(如打开页面→滑动查找→触发操作),导致脚本冗长且易失效。Kea2 通过 前置条件(@precondition) 直接定位业务功能入口,跳过冗余路径。
-
传统脚本问题:需编写代码启动应用进入视频号→转发视频给好友等多步操作→退出视频号,进入聊天界面等多步操作→点击进入分享的视频→点击点赞按钮,到这里才开始正式执行测试,路径固定且易因界面变动失效。
-
Kea2 方案: 不需要写大量的准备脚本到达点赞按钮存在的页面,只需要Fastbot自动遍历,当遍历到存在点赞按钮的页面时,即可立即测试,代码量大幅度减少。
- Kea2优势: 只关注功能场景本身,不需要关心测试的准备现场 (setUp) 和恢复现场 (tearDown) ,代码精简
脚本
# Precondition decorator: Verify the test should only run when the "like" button with resource ID "com.tencent.mm:id/star_count_tv_first" exists on screen
@precondition(lambda self: self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/star_count_tv_first", description="喜欢").exists)
def test_finder_like(self):
"""
Test the like functionality.
Simulates clicking the like button and verifies the state change from "like" to "unlike".
"""
# Click the like button with the specified resource ID on the current screen
self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/star_count_tv_first").click()
# Assert that the like button's description changes to "Cancel like" after clicking
assert self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/star_count_tv_first", description="取消喜欢").exists
截图
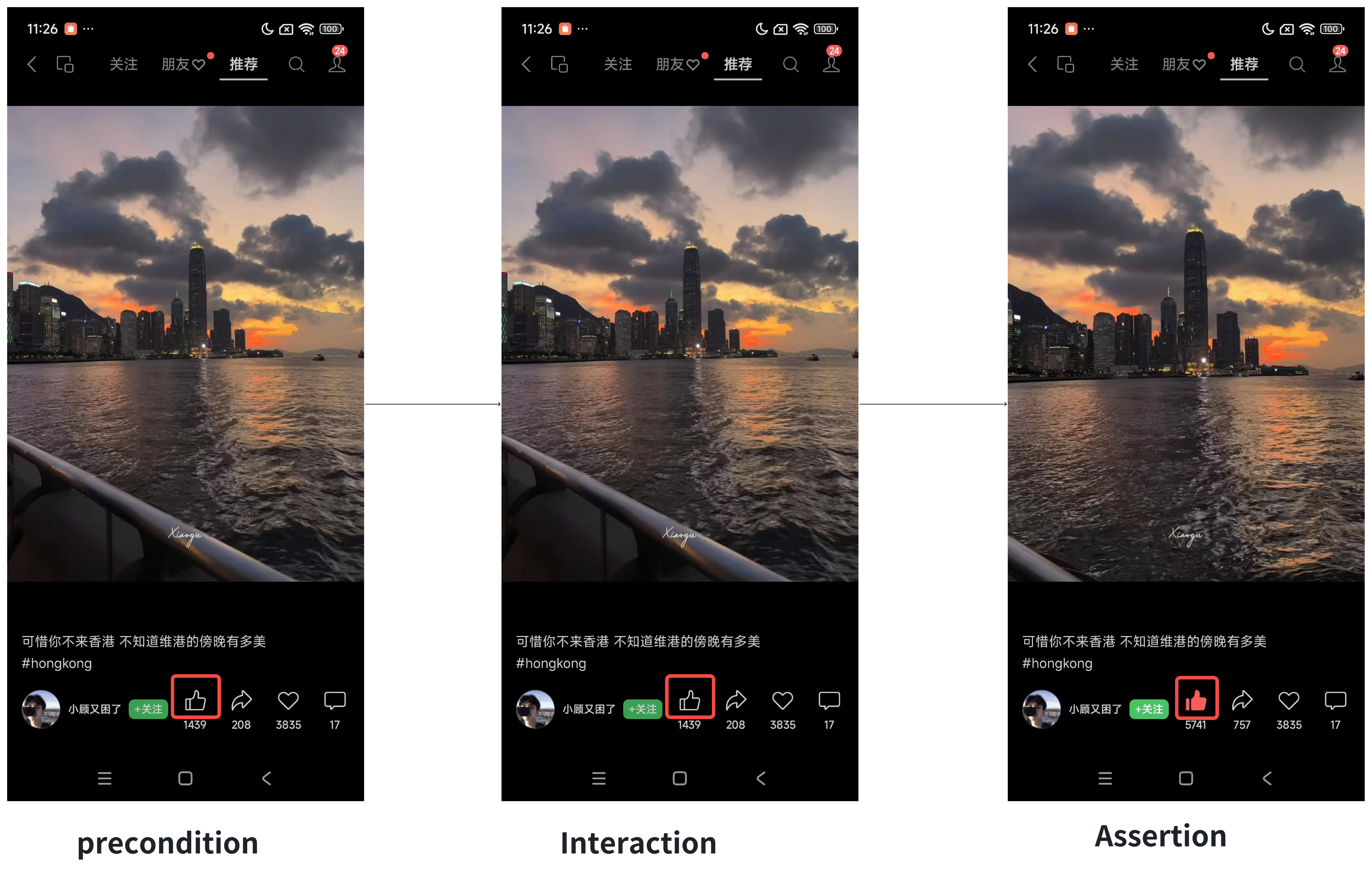
解析
前置条件:
- 当页面中存在“喜欢”按钮(通过resourceID com.tencent.mm:id/star_count_tv_first 定位),且按钮的辅助描述(description)为“喜欢”时触发测试。
交互场景:
- 点击“喜欢”按钮:执行点击操作,触发点赞功能。
断言验证:
- 验证点击后按钮的辅助描述(description)变为“取消喜欢”,表明点赞操作成功且状态已更新。
例2:消息转发功能
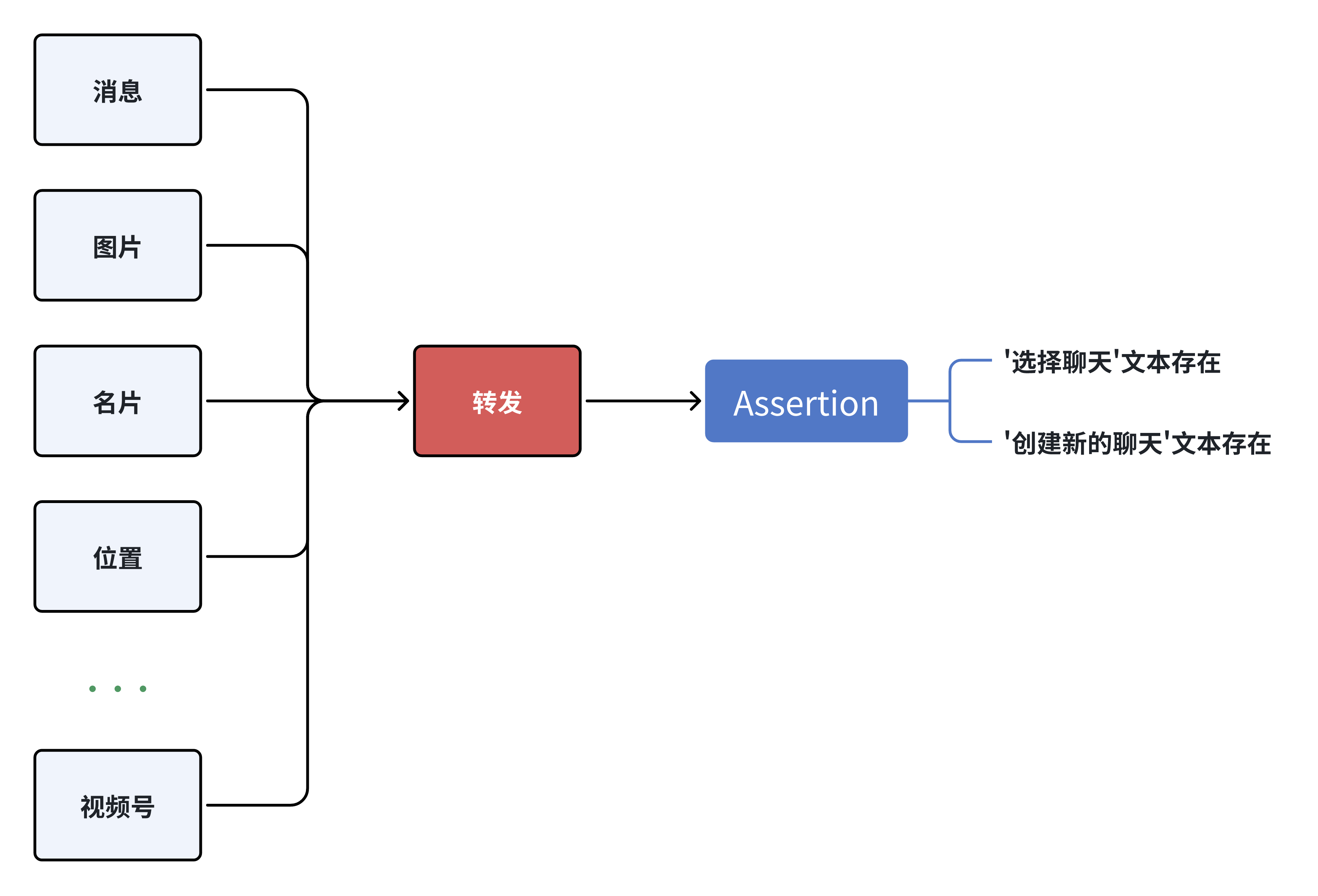
传统测试需为每个功能入口单独开发脚本(如消息转发、图片转发、名片转发、位置转发、视频号转发等),重复开发且无法验证统一业务逻辑。Kea2 只需要写一个通用性质,即可实现“一脚本多场景”覆盖。
-
传统脚本问题:需为消息转发、图片转发、名片转发、位置转发、视频号转发不同入口分别编写”转发”脚本,虽然都是测试转发功能,但是脚本并不通用,维护成本高。
-
Kea2 方案: 无论是转发什么对象,均可以通过同一个性质测试,使用性质脚本描述“转发”功能本身。有“转发”的入口按钮时即视为可执行转发操作,在执行转发操作时,其中定义操作步骤及预期行为(assert),从而检查转发功能的正确性。
-
Kea2的优势:当多个对象可执行同一个功能时,只需要编写一个功能“性质”,如此处的“转发”性质。新增业务路径时无需再次开发脚本(如:新增一个可转发的对象时,“转发”操作不变,可继续使用“转发”的性质)。
脚本
# Precondition decorator: Verify the test should only run when the "Forward" button and message input box exist on screen
@precondition(lambda self: self.d(text="转发").exists and self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/chatting_content_et").exists)
def test_forward(self):
"""
Test WeChat message forwarding functionality.
Simulates clicking the forward button and verifies the appearance of forwarding options.
"""
# Click the "Forward" button on the current screen
self.d(text="转发").click()
# Assert that the text appear after clicking
assert self.d(text="选择聊天").exists and self.d(text="创建新的聊天").exists
截图
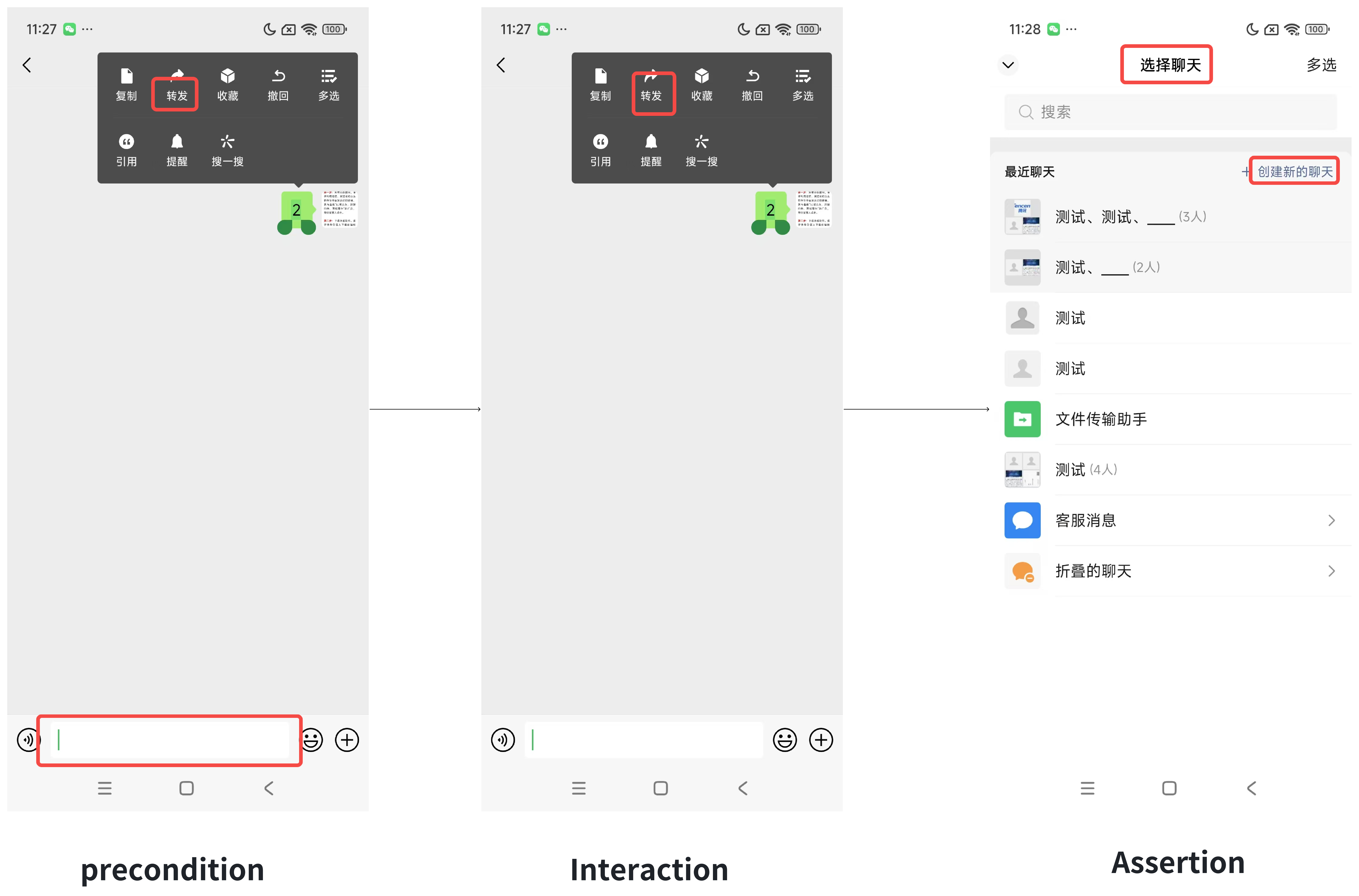
解析
前置条件:
- 当页面中同时存在“转发”按钮(text=”转发”)和聊天输入框(resourceId=”com.tencent.mm:id/chatting_content_et”)时触发测试。
交互场景:
- 点击“转发”按钮:触发转发功能,跳转至联系人选择页面。
断言验证:
- 验证成功进入联系人选择页面,页面中存在“选择聊天”按钮(text=”选择聊天”)和“创建新的聊天”按钮(text=”创建新的聊天”)。
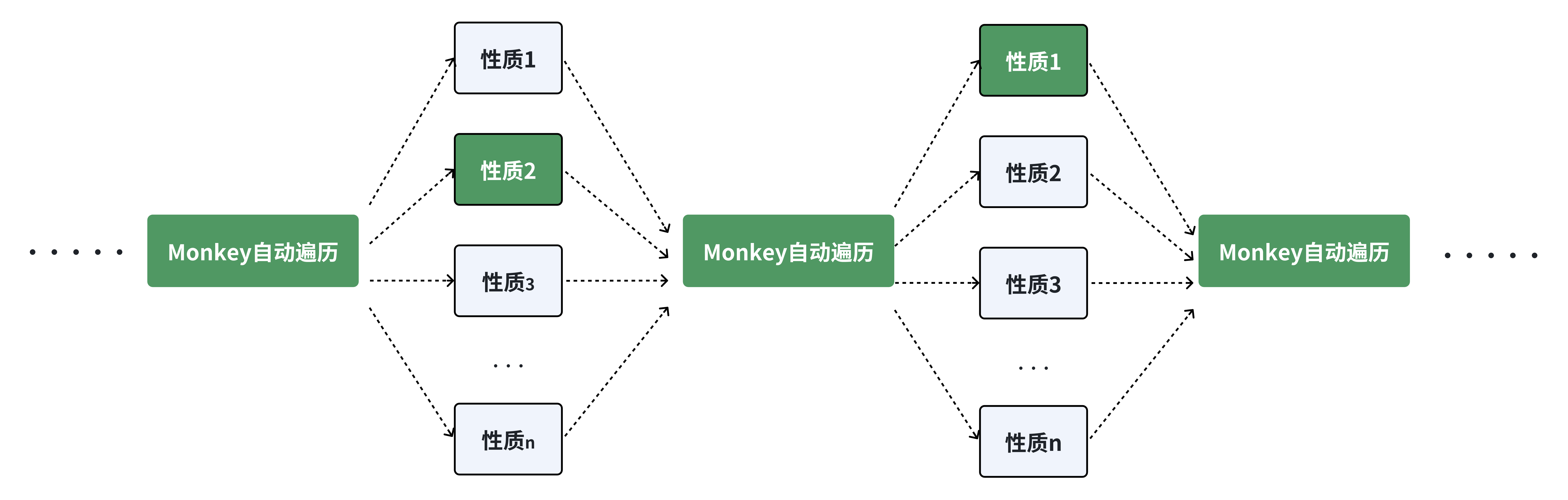
Feature 3.2:Kea2支持性质随机组合,自动生成海量测试场景
- 传统脚本的局限性
- 测试建模:将功能拆解为独立性质(如“增、删、改、查”)。
- 组合成本:若需测试路径 增→查→改→查→删→增,需手动编写完整脚本;更换路径(如 增→改→删)需重新开发脚本。
- 覆盖瓶颈:人工难以穷举所有组合,测试场景覆盖率低,且维护成本高昂。
- Kea2的解决方案
- 基础性质定义:仅需编写四个独立性质——增、删、改、查。
- 动态组合生成:遍历过程中将自动进行性质的组合(如 增→查→删、改→查→增→删 等),自动生成多样化测试路径。
- 无限场景覆盖:理论上可覆盖所有可能的操作序列,彻底解决传统脚本的路径限制问题。
例1:新增标签
脚本
# Precondition decorator:Verify the test should only run when the "新建" button and "通讯录标签" exist on screen
@precondition(lambda self: self.d(text="新建").exists and self.d(text="通讯录标签").exists)
def test_add_tag(self):
"""
Test adding a new contact tag in WeChat.
Generates a random tag name and verifies the tag is created successfully.
"""
# Click the "新建" button on the current screen
self.d(text="新建").click()
# Generate a random tag name with length between 1 and 10 characters
length = random.randint(1, 10)
random_tag_name = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_letters, k=length))
# Set the random tag name in the input field
self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/edittext").set_text(random_tag_name)
# Click the "确定" button to save the new tag
self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/next_btn",text="确定").click()
# Assert that the new tag name appears in the list after creation
assert self.d(textContains=random_tag_name, resourceId="android:id/text1").exists
截图
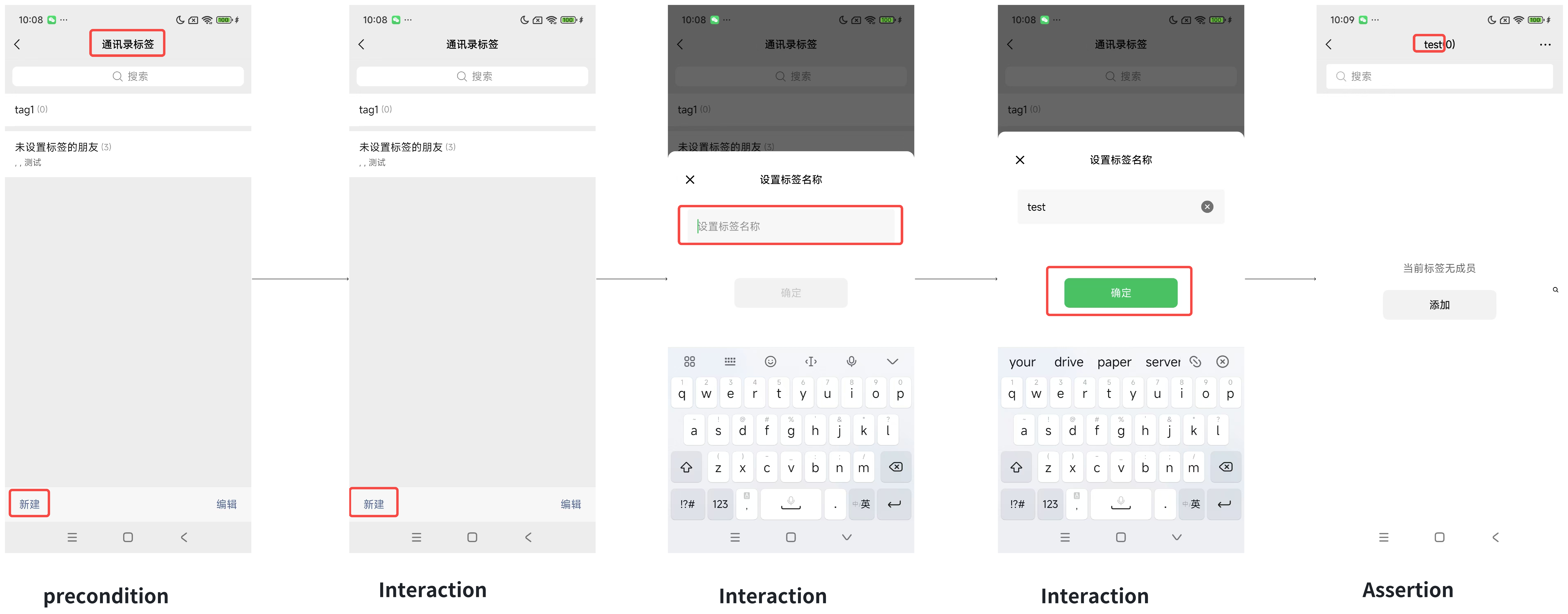
解析
前置条件:
- 当页面中同时存在“新建”按钮和“通讯录标签”文本,即当前界面是通讯录标签的首页时触发测试。
交互场景:
-
点击“新建”按钮。
-
生成随机长度的标签名(如 test)。
-
将标签名输入文本框。
-
点击“确定”按钮保存。
断言验证:
- 验证新创建的标签(如 test)出现在通讯录标签列表中。
例2:删除标签
脚本
# Precondition decorator: Verify the test should only run when there are existing tags and the "通讯录标签" exists on screen
@precondition(lambda self: len(self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title")) > 0 and self.d(text="通讯录标签").exists)
def test_del_tag(self):
"""
Test deleting a contact tag in WeChat.
Randomly selects a tag and verifies it is successfully deleted.
"""
# Randomly select a tag from the list of existing tags
tag = random.choice(self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title"))
# Get the text of the selected tag
tag_name = tag.get_text()
# Click on the selected tag
tag.click()
# Click the "更多信息" (More Information) Icon
self.d(description="更多信息").click()
# Click the "删除标签" (Delete Tag) option
self.d(text="删除标签").click()
# Confirm the deletion by clicking "删除" (Delete)
self.d(text="删除").click()
# Assert that the deleted tag no longer exists in the list
assert not self.d(text=tag_name, resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title").exists
截图
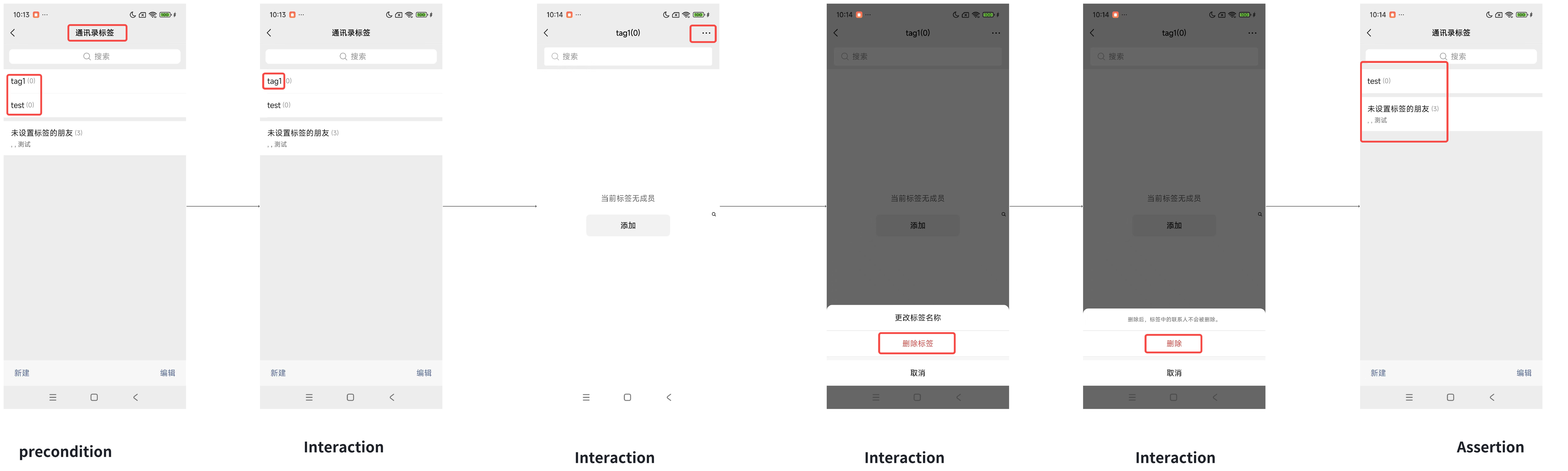
解析
前置条件:
- 当通讯录标签列表中存在至少一个标签(com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title)且页面包含“通讯录标签”文本时触发测试。
交互场景:
-
随机选择标签:从现有标签列表中随机选取一个标签(如标签名为tag1)。
-
进入操作菜单:点击该标签,打开详情页后点击“更多信息”按钮。
-
执行删除操作:点击“删除标签”选项,并点击“删除”按钮确认操作。
断言验证:
- 验证被删除的标签(如tag1)不再存在于通讯录标签列表中。
例3:重命名标签
脚本
# Precondition decorator:Verify that there are existing tags and the "通讯录标签" option is present on the screen
@precondition(lambda self: len(self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title")) > 0 and self.d(
text="通讯录标签").exists)
def test_rename_tag(self):
"""
Test renaming a contact tag in WeChat.
Randomly selects a tag, renames it, and verifies the name change is successful.
"""
# Randomly select a tag from the list of existing tags
tag = random.choice(self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title"))
# Get the current text of the selected tag
tag_name = tag.get_text()
# Click on the selected tag
tag.click()
# Click the "更多信息" (More Information) Icon
self.d(description="更多信息").click()
# Click the "更改标签名称" (Change Tag Name) option
self.d(text="更改标签名称").click()
# Generate a random new tag name with a length between 1 and 10 characters
length = random.randint(1, 10)
random_tag_name = ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_letters, k=length))
# Set the new random tag name in the input field
self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/edittext").set_text(random_tag_name)
# Click the "确定" (Confirm) button to save the new tag name
self.d(text="确定").click()
# Assert that the new tag name is displayed and the old tag name no longer exists in the list
assert self.d(textContains=random_tag_name, resourceId="android:id/text1").exists and not self.d(text=tag_name, resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title")
截图
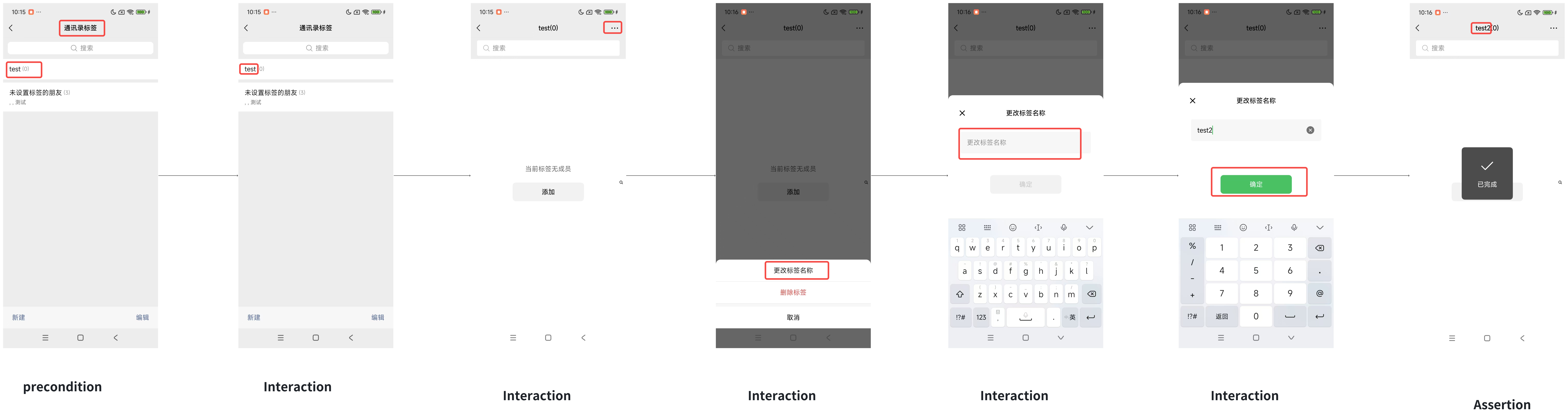
解析
前置条件:
- 当通讯录标签列表中存在至少一个标签(com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title)且页面包含“通讯录标签”文本,即当前界面是通讯录标签的首页并存在标签项时触发测试。
交互场景:
-
随机选择标签:从现有标签列表中随机选取一个标签(如原标签名为test)。
- 进入编辑模式:
- 点击标签进入详情页。
- 点击“更多信息”图标,选择“更改标签名称”。
- 输入新名称:
- 生成随机长度的新标签名(如 test2)。
- 在输入框中输入新名称,点击“确定”保存。
断言验证:
- 新标签名(如 test2)出现在列表中(通过 textContains 模糊匹配),且原标签名(如test)不再存在于列表中。
例4:搜索标签
脚本
# Precondition decorator:Verify that there are existing tags and the "通讯录标签" option is present on the screen
@precondition(lambda self: len(self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title")) > 0 and self.d(
text="通讯录标签").exists)
def test_search_tag(self):
"""
Test searching for a contact tag in WeChat.
Simulates entering a tag name and verifies the search result.
"""
# Click the "搜索" (Search) button to activate the search function
self.d(text="搜索").click()
# Enter the search text "test" into the search input field
self.d(resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/edittext").set_text("test")
# Assert that the search result displays the tag with the text "test"
assert self.d(text="test", resourceId="com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title").exists
截图
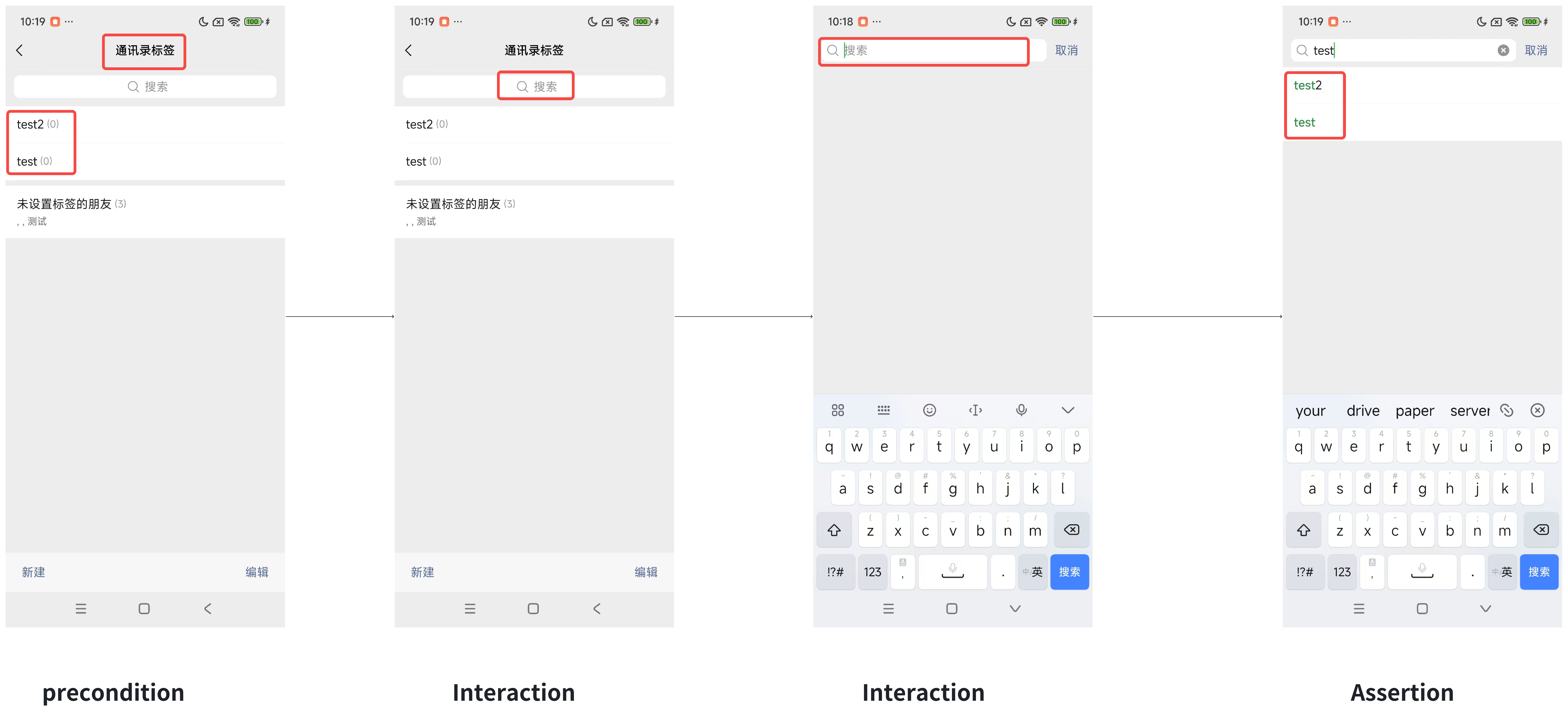
解析
前置条件:
- 当通讯录标签列表中存在至少一个标签(com.tencent.mm:id/label_item_title)且页面包含“通讯录标签”文本,即当前界面是通讯录标签的首页并存在标签项时触发测试。
交互场景:
-
进入搜索模式:点击“搜索”按钮。
-
输入关键字:在搜索框中输入固定文本test。
断言验证:
- 验证搜索结果的标签列表中存在包含文本test的标签项。